In the following article, we will discuss the important driving control system, proportional solenoids of proportional valves, the electromechanical converter that converts electrical signal into displacement signals.
Proportional Solenoid Background
In hydraulic control systems, the most important controlled parameters are the pressure and the flow. And the basic means to control the pressure and flow is to control the flow resistance. The ideal technology to control the flow resistance is direct electro-hydraulic conversion. The direct electro-hydraulic conversion technology uses a type of fluid media called electric viscous hydraulic oil which is viscous sensitive to electrical signals to realize the conversion of electric liquid viscosity. Therefore, it can control the flow resistance, which means the hydraulic control system successfully controls the pressure and flow. Apparently, this types of flow resistance control method are more easy and convenient, there is no need for electromechanical converters. But right now, the direct electro-hydraulic conversion technology is not able to reach the actual practical stage.
Based on the current production technology, to control the flow resistance is realized by the indirect electro-hydraulic conversion of electro-mechanical converters which turn the input electrical signal into mechanical movement. Electro-mechanical converters are the main components of proportional valves. The main function of electromechanical converters is to convert the amplified input electrical signals into the mechanical movement based on a certain prorate. According to the different controlled subjects or the different hydraulic parameters, in one way, the force can be passed to a spring of the pressure valve, and pre-compression of the spring is carried out. In another way, the comparison among output force, torque, and spring force can create a small displacement which is proportional to the electric circuit. Therefore, it can control the movement of spool of hydraulic valves in order to change the hydraulic resistance of the controlled flow resistance. Thus, it can be seen, electro-mechanical converters are the actuating device of hydraulic proportional valves. The static and dynamic characteristics of electromechanical converters are important for the design and performance of the complete hydraulic proportional valves.
Electro-mechanical Converters Types
There are many different dimensions to classify electro-mechanical converters.
Based on the working principle of electromechanical converters and the features of magnetic system, electro-mechanical converters can be divided as: electromagnetic type, induction type, electro-dynamic type, solenoid type, permanent magnet type, polarized type, moving coil type, moving iron type, DC type, AC type.
Based on the structure and performance of electromechanical converters, there are on-off solenoid, proportional solenoid, moving coil type motor, torque motor, stepping motor, etc.

Proportional Solenoid Basic
For hydraulic proportional valves, the most popular electro-mechanical converter is proportional solenoids.
The function of proportional solenoids is to convert the electrical signal output by proportional control amplifiers into force or displacement. Proportional solenoids hold the advantages of large thrust force, simple structure, undemanding hydraulic oil cleanliness, easy maintenance, low cost, etc. The armature field of proportional solenoid can be designed to sustain high pressure. Hydraulic proportional solenoid is the most widely used electro-mechanical converter for hydraulic proportional control element. With its features and working stability, proportional solenoid is one of the main components of hydraulic proportional control system which shows strong influence to the performance of hydraulic proportional control system and its elements.
Proportional Solenoid Structure
Proportional solenoid is consist of solenoid coil, armature, plunger, the case, etc.
When the signal enters into the solenoid coils, the magnetic field inside the coils will create an active force to the armature. Then the armature will move in the magnetic field proportionally and continuously based on the size and direction of the signal current. Next, the movement of armature will drive the movement of the plunger, which controls the movement of proportional slide valve spool.
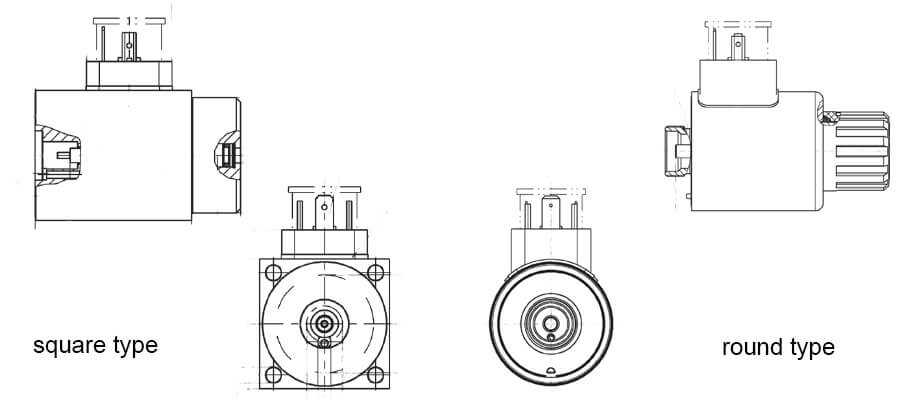
Proportional Solenoid Types
Based on the proportional solenoid working principles, proportional solenoid can be divided into three types.
Force control type proportional solenoid
The stroke of the force control type proportional solenoid is short. The output force is in proportion to the input electric current. This type of proportional solenoid usually used for the pilot control state of proportional valves.
Stroke control type proportional solenoid
The stroke control type proportional solenoid is consist of force control type proportional solenoid and the loading spring. Firstly, solenoid output force converts into displacement through the spring, the output displacement is in proportion to the input electrical current. Typically, the working stroke of the stroke control type proportional solenoid is 3mm, which has good linearity and mainly used for direct controlled proportional valves.
Position control type proportional solenoid
After the sensor detects the position of armature, it will send a feedback signal inside the valve, and after the comparison inside the valve, it will reset the position of armature. This type of proportional solenoid creates a closed loop system inside the valve, which has high precision, and the position of armature has nothing to do with the force. The position control type proportional solenoid has been widely used for Bosch proportional valves and Atos proportional valves.