A solenoid is a device that can create electromagnetism after it has been electrified. When we were young, everyone probably had assembled a solenoid on a physics class before. It is a metal core wounded with copper wires.
Someone has brought the electromagnetism technology into mechanical engineering. In machine engineering field, solenoids are a large range of actuators that convert the electric signal into mechanical movements. Solenoids are used to actuate solenoid valves, it is the control system of solenoid valves. Solenoids can be used in both pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
The Definition of a Solenoid
The solenoid is a type of non-permanent magnet, the magnetism of solenoids can be easily started and eliminated through the on and off of the power. Solenoids, also known as electromagnets, is a device with solenoid coil winding by copper wires and the solenoid tube assembly which has the plunger in it. Solenoids can be used in a large range of systems, such as hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, cars, household appliances, public facilities, etc.
Different systems need different types of solenoids, in the following part, we will discuss the various solenoid types.
Different Types of Solenoids
As solenoids have to be applied in many different areas, there are many different solenoid designs to make the solenoids suitable for different applications. Different solenoids have their unique properties for the precise operations.
There are many different ways to classify solenoid types:
According to different solenoid shapes, there are square solenoids and round solenoids.
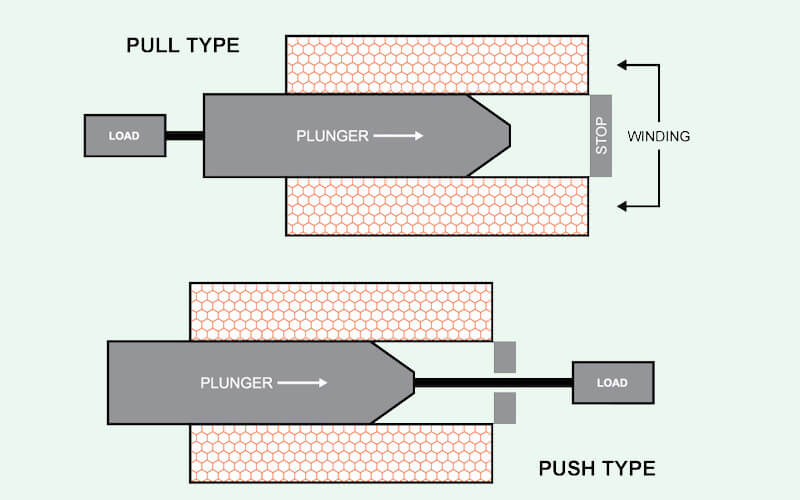
According to different solenoid characteristics, there are push-pull type solenoids, holding solenoids, rotary solenoids, tapping solenoids, etc.
According to different application fields, there are solenoids for office equipment, solenoids for cars (such as starter solenoids), solenoids for medical facilities, solenoids for household appliance industry, solenoids for textile equipment, solenoids for security systems, solenoids for valves, etc.
Despite the above solenoid types, there are also ac solenoids which are used in alternating current, and dc solenoids which are used in direct current. Different solenoids use different types of materials, adopt different solenoid designs and have different functions. But the majority of solenoids have the same basic working principles.

How A Solenoid Works
A solenoid is an electromagnetic device consists of solenoid coil and solenoid tube assembly. The solenoid coil is a coil winded with copper wires, and when the solenoid coil has been electrified, the winding copper wire will create strong magnetic force. Solenoid tube assembly has an iron plunger in the center. The solenoid plunger is movable, therefore, when the solenoid coil is electrified, the magnetic force will push the solenoid plunger to move so that the solenoid plunger can trigger the next operation of the equipment. The solenoid plunger can be moved towards one side, or both the two sides of the solenoid coils.
Magnetic Field of A Solenoid
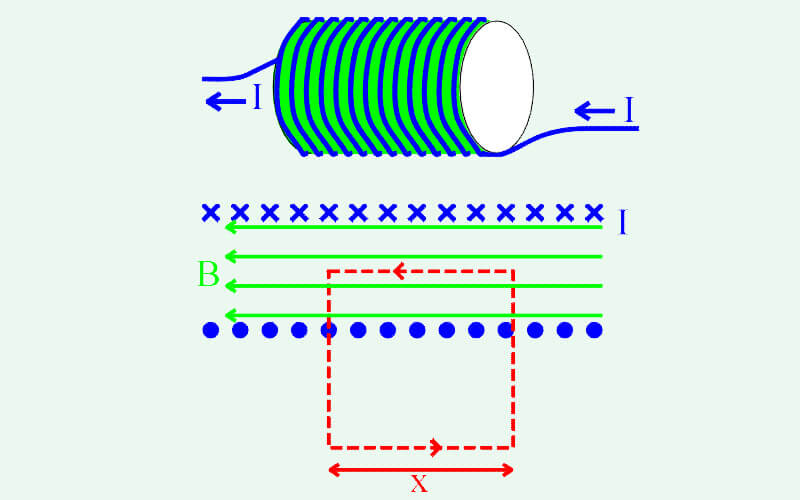
Talking about the magnetic field of a solenoid, it totally depends on the design of the solenoid coils. The solenoid coil consists of solenoid coil bobbin and copper wires. The copper wires have been wrapped around the solenoid coil bobbin, the size of the magnetic field is determined by the copper wires. The numbers of the copper wire wrap determined the size of the magnetic field of the solenoid. More wraps of copper wires can create larger magnetic force. For the most common valve solenoids, the rated stroke of valve solenoids are short, so the magnetic force of valve solenoids must be controlled precisely.
Despite the numbers of wraps of copper wires, the size of the current is also proportional to the size of the solenoid coil magnetic force.
Application of Solenoids
Solenoid technology has been adopted in numerous types of industries, it is a basic part of industrial inductors, valves, security systems, etc. It can be used in many industries, such as oil industry, transportation industry, highway guardrail, car industry, The magnetic force of solenoids is controlled by the electricity, when you turn on the electricity, the solenoid is magnetized immediately, when the power has been cut off, the solenoid becomes unmagnetized. In the following parts, we will talk about several main applications of solenoids.
Solenoids can be used to control both pneumatic and hydraulic valves. To control hydraulic valves, we have hydraulic solenoids to do the work. There are many different types of hydraulic solenoids, such as on-off solenoids, proportional solenoids, cartridge solenoids, etc. Different hydraulic solenoids control different hydraulic valves, such as on-off solenoids for directional valves, proportional solenoids for proportional valves, cartridge solenoids for cartridge valves.
Solenoids can be used in door-locking systems. Some door-locking systems adopt an electromagnetic design which needs a solenoid to trigger the locks, it is much safer than the normal locks.
Solenoids can be used in different equipment, such as cars, printers, textile machines, airplanes, fuel injection gears, even the aerospace equipment.

